简介
GeaFlow API是对高阶用户提供的开发接口,其支持Graph API和Stream API两种类型:
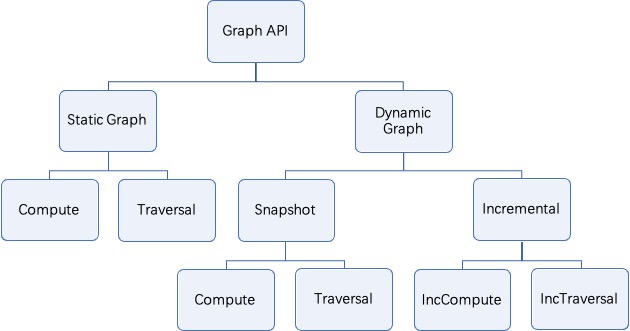
- Graph API:Graph是GeaFlow框架的一等公民,当前GeaFlow框架提供了一套基于GraphView的图计算编程接口,包含图构建、图计算及遍历。在GeaFlow中支持Static Graph和Dynamic Graph两种类型。
- Static Graph API:静态图计算API,基于该类API可以进行全量的图计算或图遍历。
- Dynamic Graph API:动态图计算API,GeaFlow中GraphView是动态图的数据抽象,基于GraphView之上,可以进行动态图计算或图遍历。同时支持对Graphview生成Snapshot快照,基于Snapshot可以提供和Static Graph API一样的接口能力。
- Stream API:GeaFlow提供了一套通用计算的编程接口,包括source构建、流批计算及sink输出。在GeaFlow中支持Batch和Stream两种类型。
- Batch API:批计算API,基于该类API可以进行批量计算。
- Stream API:流计算API,GeaFlow中StreamView是动态流的数据抽象,基于StreamView之上,可以进行流计算。
通过两种类型API的介绍可以看到,GeaFlow内部通过View统一了图视图和流视图语义。同时为了统一支持动态和静态计算两套API,GeaFlow内部抽象了Window的概念,即从Source API开始就必须带有Window,用以基于Window的方式切分数据窗口。
- 对于流或动态图API来说,Window可以按照size来切分,每个窗口读取一定size的数据,从而实现流式增量的计算。
- 对于批或静态图API来说,Window将采用AllWindow模式,一个窗口将读取全量数据,从而实现全量的计算。
Maven依赖
开发GeaFlow API应用需要添加一下maven依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.antgroup.tugraph</groupId>
<artifactId>geaflow-api</artifactId>
<version>0.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.antgroup.tugraph</groupId>
<artifactId>geaflow-pdata</artifactId>
<version>0.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.antgroup.tugraph</groupId>
<artifactId>geaflow-cluster</artifactId>
<version>0.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.antgroup.tugraph</groupId>
<artifactId>geaflow-on-local</artifactId>
<version>0.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.antgroup.tugraph</groupId>
<artifactId>geaflow-pipeline</artifactId>
<version>0.1</version>
</dependency>
功能概览
Graph API
Graph API是GeaFlow中的一等公民,其提供了一套基于GraphView的图计算编程接口,包含图构建、图计算及遍历。具体的API说明如下表格所示:
| 类型 | API | 说明 |
| 动态图 | PGraphView init(GraphViewDesc graphViewDesc) | 传入graphViewDesc进行初始化 |
| PGraphView PIncGraphView appendVertex(PWindowStream vertexStream) | 将分布式vertex流作为graphview增量的图点集 | |
| PIncGraphView appendEdge(PWindowStream edgeStream) | 将分布式edge流作为graphview增量的图边集 | |
| PIncGraphView appendGraph(PWindowStream vertexStream, PWindowStream edgeStream) | 将分布式vertex、edge流作为graphview增量的图点/边集 | |
| PGraphTraversal incrementalTraversal(IncVertexCentricTraversal incVertexCentricTraversal) | 在动态graphview上进行增量图遍历 | |
| PGraphCompute incrementalCompute(IncVertexCentricCompute incVertexCentricCompute) | 在动态graphview上进行增量图计算 | |
| void materialize() | 将动态graphview中增量的点边集合物化存储到state中 | |
| 静态图 | PGraphCompute compute(VertexCentricCompute vertexCentricCompute) | 在Graph上进行静态图VC计算 |
| PGraphWindow compute(ScatterGatherCompute sgAlgorithm, int parallelism) | 在Graph上进行静态图SG计算 | |
| PGraphTraversal traversal(VertexCentricTraversal vertexCentricTraversal) | 在Graph上进行静态图VC遍历 | |
| PWindowStream getEdges() | 返回edge集合 | |
| PWindowStream getVertices() | 返回vertex集合 |
Stream API
Stream API提供了一套通用计算的编程接口,包括source构建、流批计算及sink输出。具体的API说明如下表格所示:
| 类型 | API | 说明 |
| 流 | PStreamView init(IViewDesc viewDesc) | 传入StreamViewDesc进行初始化 |
| PIncStreamView append(PWindowStream windowStream) | 将分布式数据作为streamView增量的数据集 | |
| PWindowStream reduce(ReduceFunction reduceFunction) | 在动态streamView上进行增量reduce聚合计算 | |
| PWindowStream aggregate(AggregateFunction aggregateFunction) | 在动态streamView上进行增量aggregate聚合计算 | |
| 批 | PStreamView PWindowStream map(MapFunction mapFunction) | 进行map操作 |
| PWindowStream filter(FilterFunction filterFunction) | 进行filter操作 | |
| PWindowStream flatMap(FlatMapFunction flatMapFunction) | 进行flatmap操作 | |
| PWindowStream union(PStream uStream) | 将两个流进行union合并 | |
| PWindowBroadcastStream broadcast() | 将流广播到下游 | |
| PWindowKeyStream keyBy(KeySelector selectorFunction) | 按照selectorFunction规则进行keyby | |
| PStreamSink sink(SinkFunction sinkFunction) | 将结果输出 | |
| PWindowCollect collect() | 触发数据结果的收集 | |
| PWindowStream reduce(ReduceFunction reduceFunction) | 进行一个window内的reduce聚合计算 | |
| PWindowStream aggregate(AggregateFunction aggregateFunction) | 进行一个window内的aggregate聚合计算 | |
| PIncStreamView materialize() | 将PWindowKeyStream作为动态streamView,默认keyby后生成IncstreamView |
典型示例
PageRank动态图计算示例介绍
PageRank的定义
PageRank算法最初作为互联网网页重要度的计算方法,1996年由Page和Brin提出,并用于谷歌搜索引擎的网页排序。事实上,PageRank 可以定义在任意有向图上,后来被应用到社会影响力分析、文本摘要等多个问题。 假设互联网是一个有向图,在其基础上定义随机游走模型,即一阶马尔可夫链,表示网页浏览者在互联网上随机浏览网页的过程。假设浏览者在每个网页依照连接出去的超链接以等概率跳转到下一个网页,并在网上持续不断进行这样的随机跳转,这个过程形成一阶马尔可夫链。PageRank表示这个马尔可夫链的平稳分布。每个网页的PageRank值就是平稳概率。 算法实现思路:1.假设图中每个点的初始影响值相同;2.计算每个点对其他点的跳转概率,并更新点的影响值;3.进行n次迭代计算,直到各点影响值不再变化,即收敛状态。
实例代码
public class IncrGraphCompute {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(IncrGraphCompute.class);
// 计算结果路径
public static final String RESULT_FILE_PATH = "./target/tmp/data/result/incr_graph";
// 结果对比路径
public static final String REF_FILE_PATH = "data/reference/incr_graph";
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 获取执行环境
Environment environment = EnvironmentFactory.onLocalEnvironment();
// 执行作业提交
IPipelineResult result = submit(environment);
// 等待执行完成
result.get();
// 关闭执行环境
environment.shutdown();
}
public static IPipelineResult<?> submit(Environment environment) {
// 构建任务执行流
final Pipeline pipeline = PipelineFactory.buildPipeline(environment);
// 获取作业环境配置
Configuration envConfig = environment.getEnvironmentContext().getConfig();
// 指定保存计算结果的路径
envConfig.put(FileSink.OUTPUT_DIR, RESULT_FILE_PATH);
// graphview 名称
final String graphName = "graph_view_name";
// 创建增量图 graphview
GraphViewDesc graphViewDesc = GraphViewBuilder
.createGraphView(graphName)
// 设置 graphview 分片数, 可从配置中指定
.withShardNum(envConfig.getInteger(ExampleConfigKeys.ITERATOR_PARALLELISM))
// 设置 graphview backend 类型
.withBackend(BackendType.RocksDB)
// 指定 graphview 点边以及属性等schema信息
.withSchema(new GraphMetaType(IntegerType.INSTANCE, ValueVertex.class, Integer.class, ValueEdge.class, IntegerType.class))
.build();
// 将创建好的graphview信息添加到任务执行流
pipeline.withView(graphName, graphViewDesc);
// 提交任务并执行
pipeline.submit(new PipelineTask() {
@Override
public void execute(IPipelineTaskContext pipelineTaskCxt) {
Configuration conf = pipelineTaskCxt.getConfig();
// 1. 构建点数据输入源
PWindowSource<IVertex<Integer, Integer>> vertices =
// extract vertex from edge file
pipelineTaskCxt.buildSource(new RecoverableFileSource<>("data/input/email_edge",
// 指定每行数据的解析格式
line -> {
String[] fields = line.split(",");
IVertex<Integer, Integer> vertex1 = new ValueVertex<>(
Integer.valueOf(fields[0]), 1);
IVertex<Integer, Integer> vertex2 = new ValueVertex<>(
Integer.valueOf(fields[1]), 1);
return Arrays.asList(vertex1, vertex2);
}), SizeTumblingWindow.of(10000))
// 指定点数据source并发数
.withParallelism(pipelineTaskCxt.getConfig().getInteger(ExampleConfigKeys.SOURCE_PARALLELISM));
// 2. 构建边数据输入源
PWindowSource<IEdge<Integer, Integer>> edges =
pipelineTaskCxt.buildSource( new RecoverableFileSource<>("data/input/email_edge",
// 指定每行数据的解析格式
line -> {
String[] fields = line.split(",");
IEdge<Integer, Integer> edge = new ValueEdge<>(Integer.valueOf(fields[0]),
Integer.valueOf(fields[1]), 1);
return Collections.singletonList(edge);
}), SizeTumblingWindow.of(5000))
// 指定边数据source并发数
.withParallelism(pipelineTaskCxt.getConfig().getInteger(ExampleConfigKeys.SOURCE_PARALLELISM));
// 获取定义的graphview, 并构建图数据
PGraphView<Integer, Integer, Integer> fundGraphView =
pipelineTaskCxt.getGraphView(graphName);
PIncGraphView<Integer, Integer, Integer> incGraphView =
fundGraphView.appendGraph(vertices, edges);
// 获取作业执行map算子的并发数
int mapParallelism = pipelineTaskCxt.getConfig().getInteger(ExampleConfigKeys.MAP_PARALLELISM);
// 获取作业执行sink算子的并发数
int sinkParallelism = pipelineTaskCxt.getConfig().getInteger(ExampleConfigKeys.SINK_PARALLELISM);
// 创建sink方法
SinkFunction<String> sink = ExampleSinkFunctionFactory.getSinkFunction(conf);
// 基于图算法,执行动态图计算
incGraphView.incrementalCompute(new IncGraphAlgorithms(3))
// 获取结果点数据并作map操作
.getVertices()
.map(v -> String.format("%s,%s", v.getId(), v.getValue()))
.withParallelism(mapParallelism)
.sink(sink)
.withParallelism(sinkParallelism);
}
});
return pipeline.execute();
}
// 创建Pagerank动态图算法
public static class IncGraphAlgorithms extends IncVertexCentricCompute<Integer, Integer,
Integer, Integer> {
public IncGraphAlgorithms(long iterations) {
// 设置算法最大迭代次数
super(iterations);
}
@Override
public IncVertexCentricComputeFunction<Integer, Integer, Integer, Integer> getIncComputeFunction() {
// 指定Pagerank计算逻辑
return new PRVertexCentricComputeFunction();
}
@Override
public VertexCentricCombineFunction<Integer> getCombineFunction() {
return null;
}
}
public static class PRVertexCentricComputeFunction implements
IncVertexCentricComputeFunction<Integer, Integer, Integer, Integer> {
private IncGraphComputeContext<Integer, Integer, Integer, Integer> graphContext;
// init方法, 获取graphContext
@Override
public void init(IncGraphComputeContext<Integer, Integer, Integer, Integer> graphContext) {
this.graphContext = graphContext;
}
// 第一轮迭代evolve方法实现
@Override
public void evolve(Integer vertexId,
TemporaryGraph<Integer, Integer, Integer> temporaryGraph) {
// 动态图版本指定为0
long lastVersionId = 0L;
// 从增量图中获取id等于 vertexId 的点
IVertex<Integer, Integer> vertex = temporaryGraph.getVertex();
// 获取历史底图
HistoricalGraph<Integer, Integer, Integer> historicalGraph = graphContext
.getHistoricalGraph();
if (vertex == null) {
// 如果增量图中不存在id 等于 vertexId 的点, 就从历史图中获取
vertex = historicalGraph.getSnapShot(lastVersionId).vertex().get();
}
if (vertex != null) {
// 从增量图中获取点对应的所有出边
List<IEdge<Integer, Integer>> newEs = temporaryGraph.getEdges();
// 从历史图中获取点对应的所有出边
List<IEdge<Integer, Integer>> oldEs = historicalGraph.getSnapShot(lastVersionId)
.edges().getOutEdges();
if (newEs != null) {
for (IEdge<Integer, Integer> edge : newEs) {
// 向增量图中所有边的终点,发送消息,内容为vertexId
graphContext.sendMessage(edge.getTargetId(), vertexId);
}
}
if (oldEs != null) {
for (IEdge<Integer, Integer> edge : oldEs) {
// 向历史图中所有边的终点,发送消息,内容为vertexId
graphContext.sendMessage(edge.getTargetId(), vertexId);
}
}
}
}
@Override
public void compute(Integer vertexId, Iterator<Integer> messageIterator) {
int max = 0;
// 迭代vertexId收到的所有消息, 并取其中的最大值
while (messageIterator.hasNext()) {
int value = messageIterator.next();
max = max > value ? max : value;
}
// 从增量图中获取id 等于vertexId的点
IVertex<Integer, Integer> vertex = graphContext.getTemporaryGraph().getVertex();
// 从历史图中获取id等于 vertexId 的点
IVertex<Integer, Integer> historyVertex = graphContext.getHistoricalGraph().getSnapShot(0).vertex().get();
// 将增量图中的点属性值和消息的最大值,两者取最大
if (vertex != null && max < vertex.getValue()) {
max = vertex.getValue();
}
// 将历史图中的点属性值和消息的最大值,两者取最大
if (historyVertex != null && max < historyVertex.getValue()) {
max = historyVertex.getValue();
}
// 更新增量图中点的属性值
graphContext.getTemporaryGraph().updateVertexValue(max);
}
@Override
public void finish(Integer vertexId, MutableGraph<Integer, Integer, Integer> mutableGraph) {
// 从增量图中获取vertexId相关的点边
IVertex<Integer, Integer> vertex = graphContext.getTemporaryGraph().getVertex();
List<IEdge<Integer, Integer>> edges = graphContext.getTemporaryGraph().getEdges();
if (vertex != null) {
// 将增量图中的点添加到图数据中。
mutableGraph.addVertex(0, vertex);
graphContext.collect(vertex);
} else {
LOGGER.info("not found vertex {} in temporaryGraph ", vertexId);
}
if (edges != null) {
// 将增量中的边添加到图数据中。
edges.stream().forEach(edge -> {
mutableGraph.addEdge(0, edge);
});
}
}
}
}
PageRank静态图计算示例介绍
实例代码
public class PageRank {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(PageRank.class);
// 计算结果路径
public static final String RESULT_FILE_PATH = "./target/tmp/data/result/pagerank";
// 结果对比路径
public static final String REF_FILE_PATH = "data/reference/pagerank";
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 获取作业执行环境
Environment environment = EnvironmentFactory.onLocalEnvironment();
// 执行作业提交
IPipelineResult<?> result = submit(environment);
result.get();
// 关闭执行环境
environment.shutdown();
}
public static IPipelineResult<?> submit(Environment environment) {
// 构建任务执行流
Pipeline pipeline = PipelineFactory.buildPipeline(environment);
// 获取作业相关配置
Configuration envConfig = environment.getEnvironmentContext().getConfig();
// 指定结果输出路径
envConfig.put(FileSink.OUTPUT_DIR, RESULT_FILE_PATH);
// 提交任务并执行
pipeline.submit((PipelineTask) pipelineTaskCxt -> {
Configuration conf = pipelineTaskCxt.getConfig();
// 1. 构建图中点的输入数据
PWindowSource<IVertex<Integer, Double>> prVertices =
pipelineTaskCxt.buildSource(new FileSource<>("data/input/email_vertex",
// 定义每行数据解析成点的格式
line -> {
String[] fields = line.split(",");
IVertex<Integer, Double> vertex = new ValueVertex<>(
Integer.valueOf(fields[0]), Double.valueOf(fields[1]));
return Collections.singletonList(vertex);
}), AllWindow.getInstance())
// 设定并发数
.withParallelism(conf.getInteger(ExampleConfigKeys.SOURCE_PARALLELISM));
// 2. 构建图中边的输入数据
PWindowSource<IEdge<Integer, Integer>> prEdges = pipelineTaskCxt.buildSource(new FileSource<>("data/input/email_edge",
// 定义每行数据解析成边的格式
line -> {
String[] fields = line.split(",");
IEdge<Integer, Integer> edge = new ValueEdge<>(Integer.valueOf(fields[0]), Integer.valueOf(fields[1]), 1);
return Collections.singletonList(edge);
}), AllWindow.getInstance())
// 设定并发数
.withParallelism(conf.getInteger(ExampleConfigKeys.SOURCE_PARALLELISM));
// 迭代计算并发数
int iterationParallelism = conf.getInteger(ExampleConfigKeys.ITERATOR_PARALLELISM);
// 定义graphview
GraphViewDesc graphViewDesc = GraphViewBuilder
.createGraphView(GraphViewBuilder.DEFAULT_GRAPH)
// 指定分片数为2
.withShardNum(2)
// 指定backend类型为memory
.withBackend(BackendType.Memory)
.build();
// 基于点边数据和定义的graphview, 构建静态图
PGraphWindow<Integer, Double, Integer> graphWindow =
pipelineTaskCxt.buildWindowStreamGraph(prVertices, prEdges, graphViewDesc);
// 获取sink函数
SinkFunction<IVertex<Integer, Double>> sink = ExampleSinkFunctionFactory.getSinkFunction(conf);
// 指定计算并发数,执行静态计算方法
graphWindow.compute(new PRAlgorithms(3))
.compute(iterationParallelism)
// 获取计算结果点,按照定义的sink函数输出
.getVertices()
.sink(sink)
.withParallelism(conf.getInteger(ExampleConfigKeys.SINK_PARALLELISM));
});
return pipeline.execute();
}
public static void validateResult() throws IOException {
ResultValidator.validateResult(REF_FILE_PATH, RESULT_FILE_PATH);
}
public static class PRAlgorithms extends VertexCentricCompute<Integer, Double, Integer, Double> {
public PRAlgorithms(long iterations) {
// 指定静态图计算的迭代次数
super(iterations);
}
@Override
public VertexCentricComputeFunction<Integer, Double, Integer, Double> getComputeFunction() {
return new PRVertexCentricComputeFunction();
}
@Override
public VertexCentricCombineFunction<Double> getCombineFunction() {
return null;
}
}
public static class PRVertexCentricComputeFunction extends AbstractVcFunc<Integer, Double, Integer, Double> {
// 静态图计算方法实现
@Override
public void compute(Integer vertexId,
Iterator<Double> messageIterator) {
// 从静态图中获取点id等于vertexId的点
IVertex<Integer, Double> vertex = this.context.vertex().get();
if (this.context.getIterationId() == 1) {
// 第一轮迭代向邻居节点发送消息,消息内容为vertexId点的属性值
this.context.sendMessageToNeighbors(vertex.getValue());
} else {
double sum = 0;
while (messageIterator.hasNext()) {
double value = messageIterator.next();
sum += value;
}
// 累积消息之和,并设置为当前点的属性值
this.context.setNewVertexValue(sum);
}
}
}
}
WordCount批计算示例介绍
实例代码
public class WordCountStream {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(WordCountStream.class);
// 计算结果路径
public static final String RESULT_FILE_PATH = "./target/tmp/data/result/wordcount";
// 结果对比路径
public static final String REF_FILE_PATH = "data/reference/wordcount";
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 获取作业执行环境
Environment environment = EnvironmentUtil.loadEnvironment(args);
// 执行作业提交
IPipelineResult<?> result = submit(environment);
result.get();
// 关闭执行环境
environment.shutdown();
}
public static IPipelineResult<?> submit(Environment environment) {
// 构建任务执行流
Pipeline pipeline = PipelineFactory.buildPipeline(environment);
// 获取作业环境配置
Configuration envConfig = environment.getEnvironmentContext().getConfig();
// 指定保存计算结果的路径
envConfig.getConfigMap().put(FileSink.OUTPUT_DIR, RESULT_FILE_PATH);
pipeline.submit(new PipelineTask() {
@Override
public void execute(IPipelineTaskContext pipelineTaskCxt) {
Configuration conf = pipelineTaskCxt.getConfig();
// 获取输入数据流
PWindowSource<String> streamSource = pipelineTaskCxt.buildSource(
new FileSource<String>("data/input/email_edge",
// 定义每行数据的解析格式
line -> {
String[] fields = line.split(",");
return Collections.singletonList(fields[0]);
// 定义数据窗口大小
}) {}, SizeTumblingWindow.of(5000))
// 定义输入数据流的并发数
.withParallelism(conf.getInteger(ExampleConfigKeys.SOURCE_PARALLELISM));
SinkFunction<String> sink = ExampleSinkFunctionFactory.getSinkFunction(conf);
streamSource
// 对流中的数据作map操作
.map(e -> Tuple.of(e, 1))
// key by
.keyBy(new KeySelectorFunc())
// reduce 聚合统计相同数据的个数
.reduce(new CountFunc())
// 指定算子并发数
.withParallelism(conf.getInteger(ExampleConfigKeys.REDUCE_PARALLELISM))
.map(v -> String.format("(%s,%s)", ((Tuple) v).f0, ((Tuple) v).f1))
.sink(sink)
.withParallelism(conf.getInteger(ExampleConfigKeys.SINK_PARALLELISM));
}
});
return pipeline.execute();
}
public static void validateResult() throws IOException {
ResultValidator.validateResult(REF_FILE_PATH, RESULT_FILE_PATH);
}
public static class MapFunc implements MapFunction<String, Tuple<String, Integer>> {
// map方法实现, 将每个输入单词转换为Tuple
@Override
public Tuple<String, Integer> map(String value) {
LOGGER.info("MapFunc process value: {}", value);
return Tuple.of(value, 1);
}
}
public static class KeySelectorFunc implements KeySelector<Tuple<String, Integer>, Object> {
@Override
public Object getKey(Tuple<String, Integer> value) {
return value.f0;
}
}
public static class CountFunc implements ReduceFunction<Tuple<String, Integer>> {
@Override
public Tuple<String, Integer> reduce(Tuple<String, Integer> oldValue, Tuple<String, Integer> newValue) {
return Tuple.of(oldValue.f0, oldValue.f1 + newValue.f1);
}
}
}
KeyAgg流计算示例介绍
实例代码
public class WindowStreamKeyAgg implements Serializable {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(WindowStreamKeyAgg.class);
// 计算结果路径
public static final String RESULT_FILE_PATH = "./target/tmp/data/result/wordcount";
// 结果对比路径
public static final String REF_FILE_PATH = "data/reference/wordcount";
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 获取作业执行环境
Environment environment = EnvironmentUtil.loadEnvironment(args);
// 执行作业提交
IPipelineResult<?> result = submit(environment);
result.get();
// 关闭执行环境
environment.shutdown();
}
public static IPipelineResult<?> submit(Environment environment) {
// 构建执行流
Pipeline pipeline = PipelineFactory.buildPipeline(environment);
// 获取作业环境配置
Configuration envConfig = environment.getEnvironmentContext().getConfig();
// 指定作业结果输出路径
envConfig.getConfigMap().put(FileSink.OUTPUT_DIR, RESULT_FILE_PATH);
// 开启动态流图materialize开关
envConfig.getConfigMap().put(FrameworkConfigKeys.INC_STREAM_MATERIALIZE_DISABLE.getKey(), Boolean.TRUE.toString());
ResultValidator.cleanResult(RESULT_FILE_PATH);
pipeline.submit(new PipelineTask() {
@Override
public void execute(IPipelineTaskContext pipelineTaskCxt) {
Configuration conf = pipelineTaskCxt.getConfig();
// 窗口大小定义为5000, 构建输入数据流
PWindowSource<String> streamSource =
pipelineTaskCxt.buildSource(new FileSource<String>("data/input"
+ "/email_edge", Collections::singletonList) {}, SizeTumblingWindow.of(5000));
SinkFunction<String> sink = ExampleSinkFunctionFactory.getSinkFunction(conf);
streamSource
.flatMap(new FlatMapFunction<String, Long>() {
@Override
public void flatMap(String value, Collector collector) {
// flatmap方法实现
String[] records = value.split(SPLIT);
for (String record : records) {
// 将每行数据切分并获取
collector.partition(Long.valueOf(record));
}
}
})
// map算子
.map(p -> Tuple.of(p, p))
// 定义特定条件的key by算子
.keyBy(p -> ((long) ((Tuple) p).f0) % 7)
.aggregate(new AggFunc())
.withParallelism(conf.getInteger(AGG_PARALLELISM))
.map(v -> String.format("%s,%s", ((Tuple) v).f0, ((Tuple) v).f1))
.sink(sink).withParallelism(conf.getInteger(SINK_PARALLELISM));
}
});
return pipeline.execute();
}
public static void validateResult() throws IOException {
ResultValidator.validateMapResult(REF_FILE_PATH, RESULT_FILE_PATH, String::compareTo);
}
public static class AggFunc implements
AggregateFunction<Tuple<Long, Long>, Tuple<Long, Long>, Tuple<Long, Long>> {
// 定义累加器实现
@Override
public Tuple<Long, Long> createAccumulator() {
return Tuple.of(0L, 0L);
}
@Override
public void add(Tuple<Long, Long> value, Tuple<Long, Long> accumulator) {
// 对相同key的两个value,累加value的f1值
accumulator.setF0(value.f0);
accumulator.setF1(value.f1 + accumulator.f1);
}
@Override
public Tuple<Long, Long> getResult(Tuple<Long, Long> accumulator) {
// 返回累加后的结果
return Tuple.of(accumulator.f0, accumulator.f1);
}
@Override
public Tuple<Long, Long> merge(Tuple<Long, Long> a, Tuple<Long, Long> b) {
return null;
}
}
}